The term "ergonomics" is Greek in origin and is a composite of two words: Ergon – work and Nomos – rule, law.
A.
Ergonomics is a science of work, i.e. a scientific discipline concerned with adjusting working environment to people’s mental and physical capacity. The aim of ergonomics is to humanize work by arranging the human being – machine – working environment system in such a way as to reduce biological cost and achieve maximum efficiency, e.g. by eliminating the root causes of occupational diseases. Ergonomics relies on the achievements of such sciences or scientific domains as occupational psychology, occupational sociology, occupational physiology, hygiene, occupational medicine, organization of work and anthropometry, as well as technical sciences, e.g. materials technology, mechanical engineering.
The basic object of research is the system composed of human being, machine and material working environment conditions, i.e. workplace conditions. The main goal pursued by ergonomics is to improve conditions of work for employees by adjusting the working environment to the employee’s capabilities, properly selecting employees for a given position and education employees in specific features associated with their workplace.
Ergonomics can be subdivided into conceptual ergonomics (incorporation of ergonomics principles at the stage of concept development and design) and corrective ergonomics (improvement of working conditions by modernizing existing workplaces (machines, equipment)).
Ergonomics has a number of applications both in the industry, office work and everyday life. At present, different fields of ergonomics encompass nearly all areas of human activity, e.g. manufacturing techniques and technologies, product quality, office work (especially computer workplaces), interior design, means of transport, sports and recreation.
Nature has not designed people for working in the office, in the sitting position, as in front of the computer. Unfortunately, contemporary life has been dominated by the sitting posture.
|
|
 |
Ergonomics substantially affects the efficiency of work of individual employees and the organization as a whole, which in turn improves the financial situation of the company.
Speaking of ergonomics, it should be noted that nearly everything is ergonomic, though to a varying degree. The higher the ergonomics of the working environment, the greater the improvement in term of:
- health and well-being,
- increased working effectiveness,
- increased efficiency of workers,
- increased creativity of thinking of employees
A highly ergonomic workplace is also a good tool for motivating employees and tying them to the company. You should note that a small investment in a better office chair, of just 10 Ls a month over 5 years, is still twice lower than washing the company car, with the added benefits of improved working comfort and relief of pain.
A properly equipped interior builds up the company’s reputation both in the eyes of customers, visiting contractors and employees. It is a major advantage for a company to have a reputation for caring about its employees, for it is people that make up the company.
In additional to legal liability, failure to create an ergonomic workplace increases company costs due to absences, medical treatments and damages. If the workplace is not ergonomic, employees suffer from increased fatigue which in turn, causes reduced efficiency of work, reduced alertness and more errors. For example, an error resulting from faulty interpretation of data may produce major economic losses and even compromise the level of safety of users of defective products.
B.
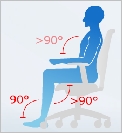
To sit properly, you need to observe a couple of simple rules of ergonomics.
 |
|
 |
|
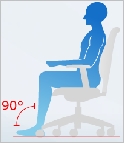 |
You feet should rest comfortably on the floor. The foot surface should form an angle of 90 degrees with the lower leg. This is possible by adjusting seat height to identify the best sitting position for people of various heights. | ||
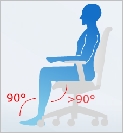 |
To allow unrestrained blood flow, the knees should form a slightly obtuse angle with the body. The position is possible thanks to a specially profiled seat with height adjustment. | ||
|
|
Height-adjustable armrests should make it possible to achieve an obtuse angle between the forearm and the arm. | ||
 |
The backrest should be slightly tilled back (the angle between the trunk and the rest of the body should be greater than 90 degrees) to allow undisturbed functioning of internal organs. | ||
 |
To prevent leg numbness and pressure on the thigh surface, you should use the entire depth of the seat. | ||
 |
The back should be in contact with a specially profiled backrest at all times, thus helping to maintain the natural curvature of the spine. | ||
 |
Sitting in the same position for prolonged periods is not advisable. Such a practice causes excessive load on the body. You should, therefore, change your position while sitting at your desk as frequently as possible, by stretching out your legs, arching your back and swinging in your chair. Dynamic posture changes during work help take the load off your locomotor’s system. |
C.
An ergonomic chair should be adjusted to the anthropometric features of each individual. It should take into account body dimensions, physiological and mental capabilities, visual needs and safety requirements.
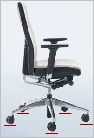 |
A chair should be stable, i.e. equipped with at least five-point support base with rollers. | |
 |
An ergonomic chair should also have a backrest that ensures stable support for the lumbar section of the back and the shoulder blades. The profiled shape of the backrest should be adjusted to individual height, while the convex of the part should reflect the height of the lumbar section. The back should, therefore, be both horizontally and vertically adjustable. | |
 |
The seat surface should be flat, with rounded front edges. The width and depth of the seat are no less important. The seat should be ca. 40 cm deep. Seat height adjustment is another essential feature (thanks to a special mechanism). |
|
 |
The chair should have armrests (with adjustable height and spacing) which are indispensable for typing. Armrests support your forearms during work and take the strain off your wrists. | |
 |
A shock absorber ensures smooth adjustment of the seat height. The comfort of sitting is additionally enhanced by using a gas shock absorbed with an integrated spring (air cushion). | |
 |
The operating mechanism of the chair should, on the one hand, provide comfortable sitting and, on the other, allow the user to freely change their body position. Dynamic posture changes while sitting are possible thanks to using the SYNCHRO system. The SYNCHRO system makes it possible to regulate the tilt angle between the backrest and the seat, with an option to adjust the flexibility of backrest tilt depending on the weight of the sitting person, and seat height adjustment. |
![]()